王昱喬-第八週作業
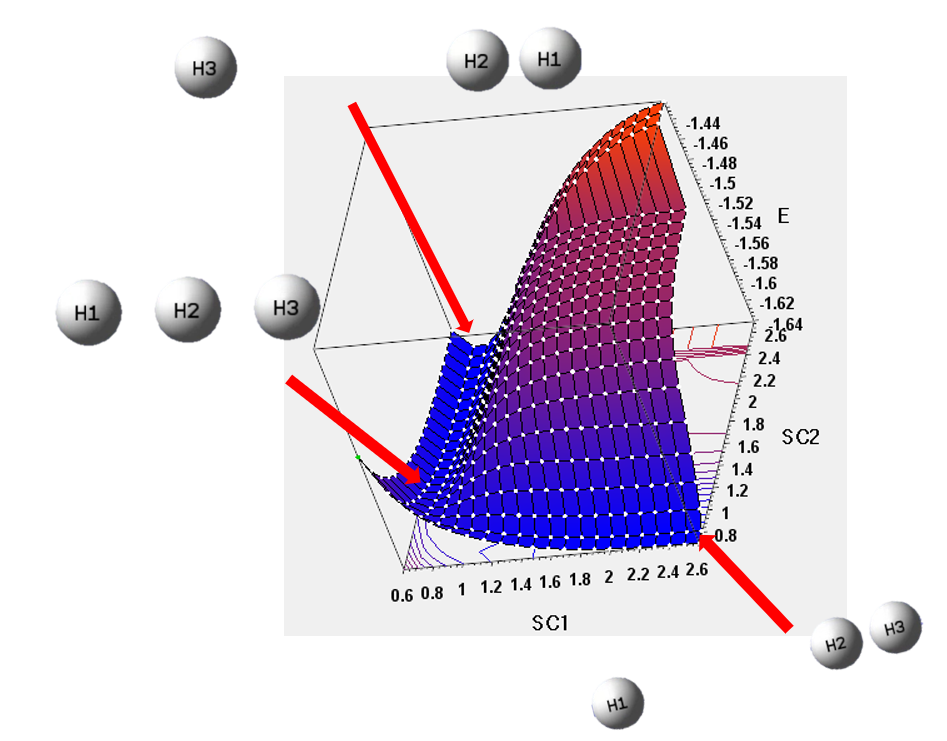
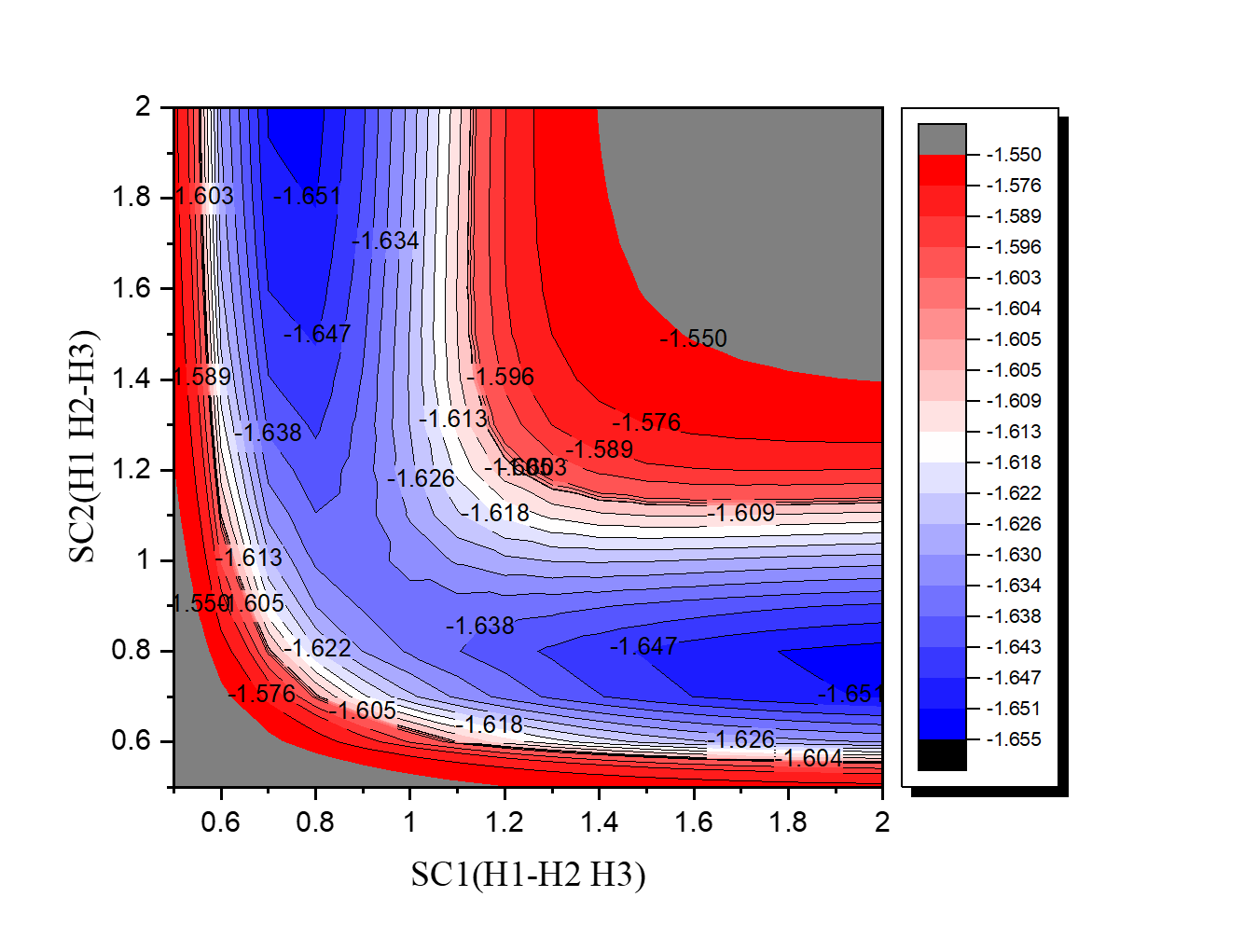
Plot potential energy curve of H2 + H → H + H2 reaction
- Use Gaussian to find the potential energy of H2 + H → H + H2.
- Collect data from the output file and use OriginPro 9 to plot the potential energy curve(2D).
- Data Link : Google Drive
SC1=bond length between H1 & H2
SC2=bond length between H2 & H3
Unit=Angstroms
Calculate the structures and atomization energies (AE) of AHn (A = H~Ne) with the following method then compare with the experimental values.
- Calculate the atomization energies by calculating A & AHn in Gaussian.
- Collect all data from the output file and use the function [A(EE)+H(EE)*n-AHn(EE)]*627.5095 ( kcal/mol ) to calculate the atomization energies (AE).
- Find the Bond length (Å) & Bond angle (degree) in the output file too.
- Calculate the atomization energies (AE) by following methods/basis set
optimization
MP2/6-31+G(d,p)
MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ
B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p)
B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
single point energy
CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
unit=kcal/mol
| Atomization energies of hydrides | |||||
| MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | Experimental value(D0) | |
| H2 | 101.2 | 103.8 | 111.7 | 110.1 | 103.3 |
| LiH | 45.2 | 51.8 | 57.2 | 58.5 | 55.7 |
| BeH2 | 141.0 | 146.0 | 155.7 | 155.3 | 149.3 |
| BH3 | 269.5 | 275.5 | 286.7 | 284.7 | 266.8 |
| CH4 | 399.4 | 411.4 | 422.8 | 420.6 | 392.4 |
| NH3 | 274.9 | 290.2 | 300.2 | 300.7 | 276.7 |
| H2O | 220.5 | 232.2 | 229.6 | 230.6 | 219.4 |
| HF | 137.3 | 143.7 | 138.4 | 139.1 | 135.4 |
| Atomization energies of hydrides | ||||
| MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | |
| H2 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 8.4 | 6.8 |
| LiH | 10.5 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 2.8 |
| BeH2 | 8.3 | 3.3 | 6.4 | 6.0 |
| BH3 | 2.7 | 8.7 | 19.9 | 17.9 |
| CH4 | 7.0 | 19.0 | 30.4 | 28.2 |
| NH3 | 1.8 | 13.5 | 23.5 | 24.0 |
| H2O | 1.1 | 12.8 | 10.2 | 11.2 |
| HF | 1.9 | 8.3 | 3.0 | 3.7 |
| 絕對誤差平均值 | 4.4 | 8.7 | 12.9 | 12.6 |
| Atomization energies of hydrides | |||||
| CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | Experimental value(D0) | |
| H2 | 108.5 | 108.6 | 108.5 | 108.6 | 103.3 |
| LiH | 56.9 | 56.9 | 56.9 | 56.9 | 55.7 |
| BeH2 | 145.1 | 145.1 | 145.1 | 145.1 | 149.3 |
| BH3 | 276.8 | 276.8 | 276.8 | 276.8 | 266.8 |
| CH4 | 428.0 | 428.0 | 428.0 | 428.0 | 392.4 |
| NH3 | 291.2 | 291.2 | 291.3 | 291.3 | 276.7 |
| H2O | 228.2 | 228.2 | 228.2 | 228.2 | 219.4 |
| HF | 139.2 | 139.2 | 139.3 | 139.3 | 135.4 |
| Atomization energies of hydrides | ||||
| CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | |
| H2 | 5.2 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.3 |
| LiH | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| BeH2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| BH3 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| CH4 | 35.6 | 35.6 | 35.6 | 35.6 |
| NH3 | 14.5 | 14.5 | 14.6 | 14.6 |
| H2O | 8.8 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 8.8 |
| HF | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
| 絕對誤差平均值 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 10.4 |
experimental value:Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark DataBase
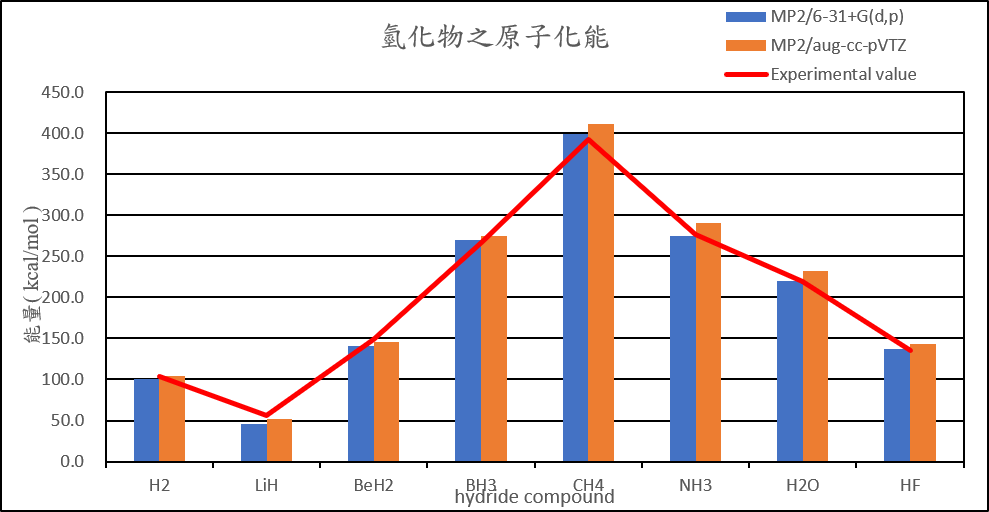
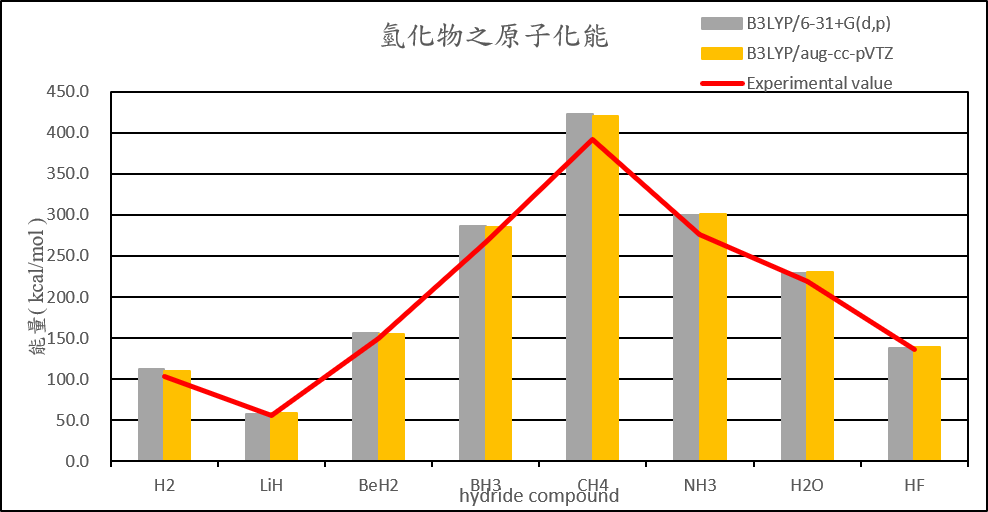
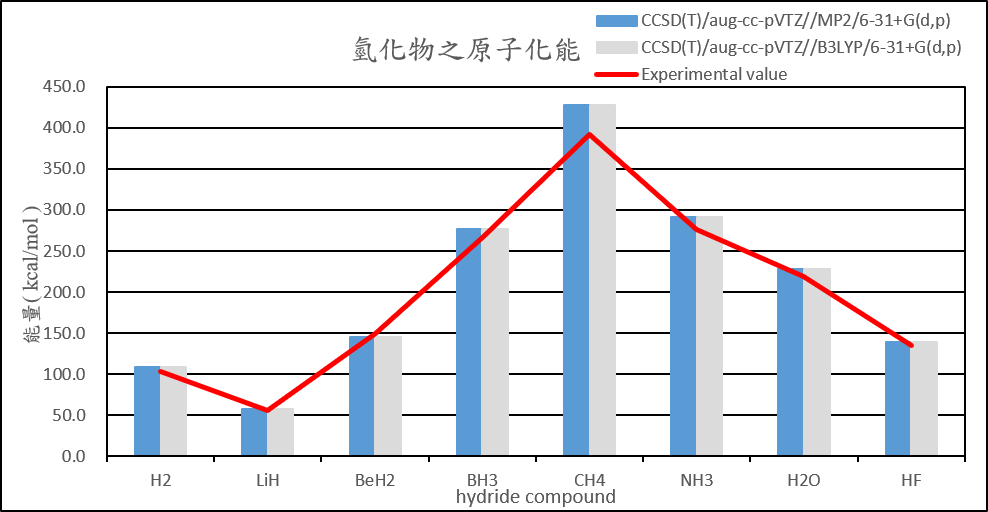
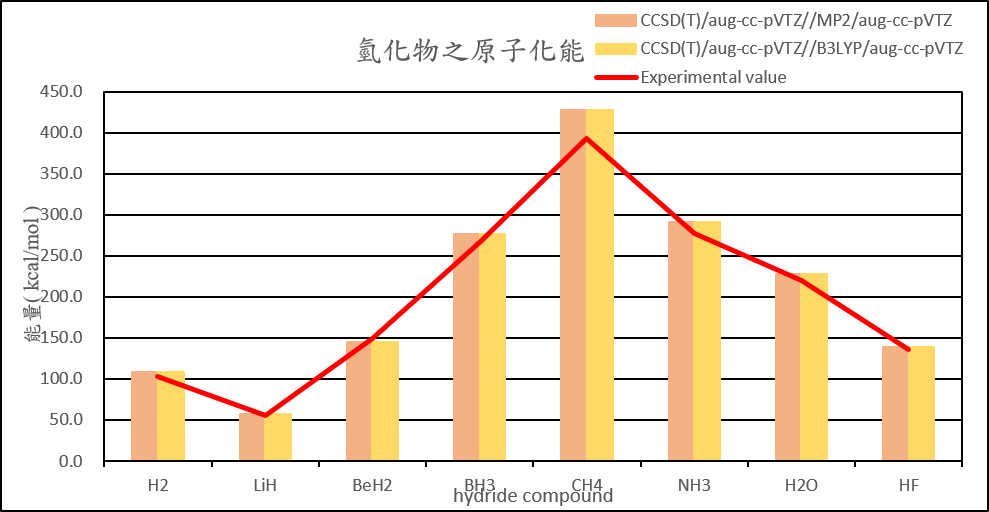
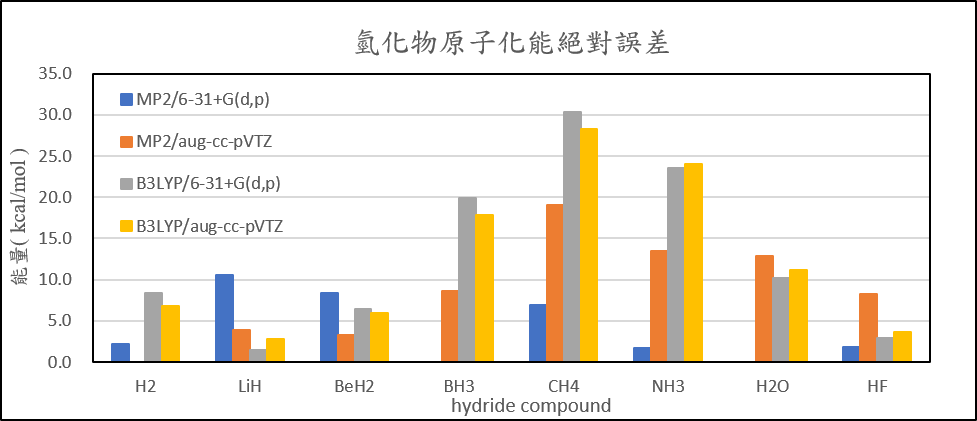
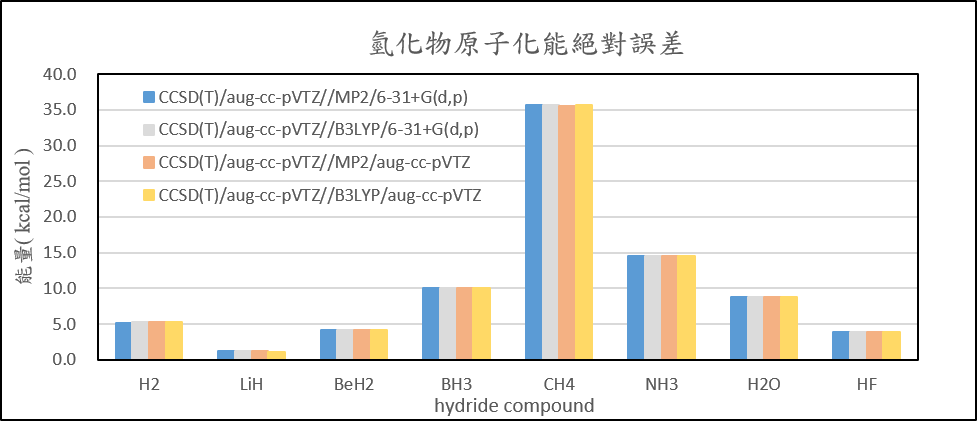
2. Calculate the structure
| Bond angle ( degree ) | |||||
| MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | Exp | |
| H2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| LiH | - | - | - | - | - |
| BeH2 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 |
| BH3 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 |
| CH4 | 109.5 | 109.5 | 109.5 | 109.5 | 109.5 |
| NH3 | 108.1 | 106.8 | 108.1 | 107.2 | 106.7 |
| H2O | 105.4 | 104.1 | 105.8 | 105.1 | 104.5 |
| HF | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bond length (Å) | |||||
| MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | Exp | |
| H2 | 0.734 | 0.737 | 0.743 | 0.743 | 0.741 |
| LiH | 1.623 | 1.605 | 1.614 | 1.590 | 1.595 |
| BeH2 | 1.328 | 1.330 | 1.331 | 1.325 | 1.326 |
| BH3 | 1.186 | 1.187 | 1.193 | 1.188 | 1.190 |
| CH4 | 1.087 | 1.086 | 1.093 | 1.088 | 1.087 |
| NH3 | 1.012 | 1.012 | 1.016 | 1.013 | 1.012 |
| H2O | 0.963 | 0.961 | 0.965 | 0.962 | 0.958 |
| HF | 0.926 | 0.922 | 0.928 | 0.924 | 0.917 |
| Absolute error of bond length (Å) | ||||
| MP2/6-31+G(d,p) | MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ | B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) | B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ | |
| H2 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| LiH | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.019 | 0.005 |
| BeH2 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| BH3 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| CH4 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.001 |
| NH3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.001 |
| H2O | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.004 |
| HF | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.007 |
| 絕對平均誤差 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.003 |
Conclusion
- when the molecule contains more hydrogen atoms, the absolute error is larger