0920HW
20220920
- Use Spartan to calculate the ionization energy of atoms with atomic number 1~18, by using PM3、HF and MP2 theoretical method with 6-31G* basis set, and do some simple statistical analysis. The unit of the ionization energy is kcal/mol .
Step1:build hydrogen atom
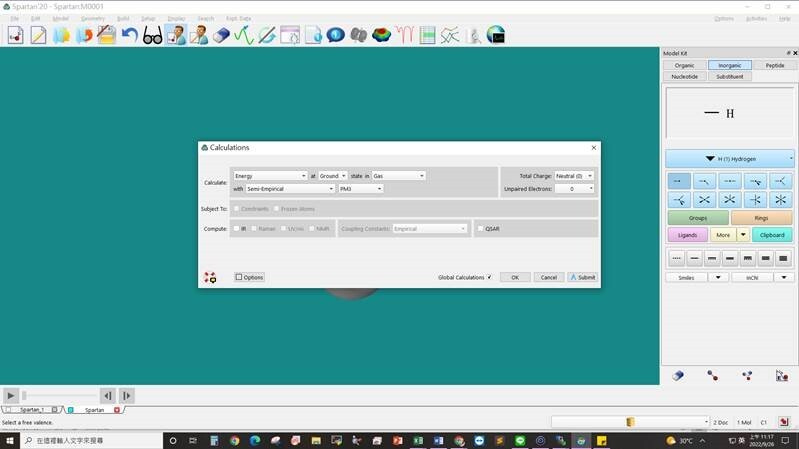
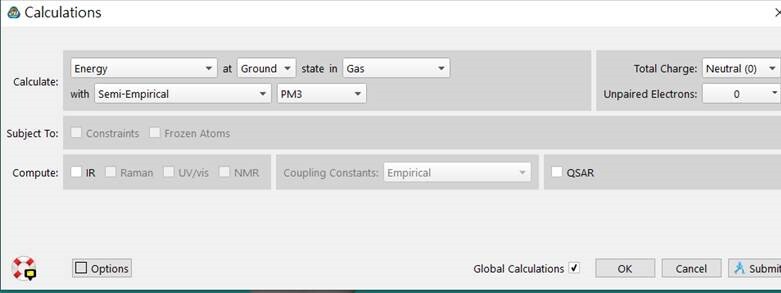
Step2: selection of calculation method, basis sets,total charge and unpaired electrons → submit
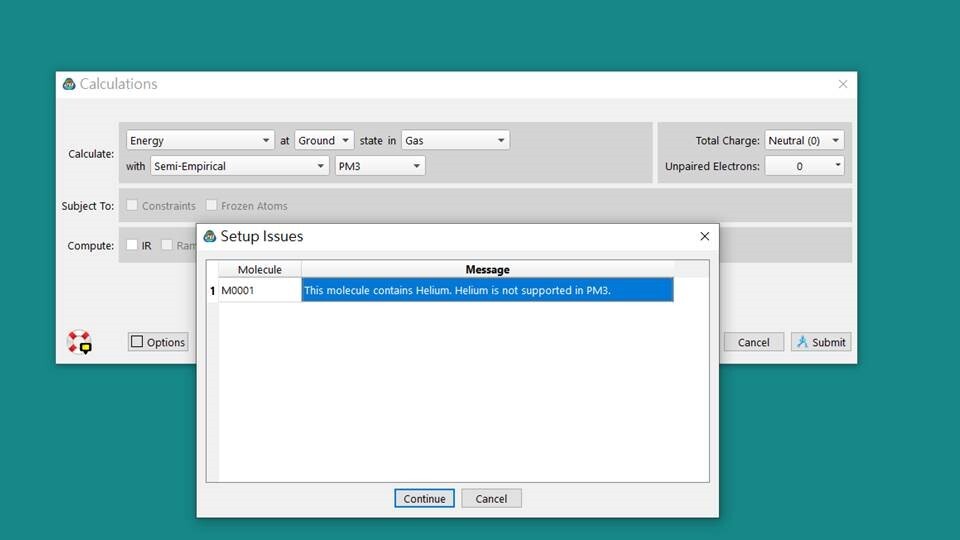
Semiempirical methods are simplified versions of Hartree-Fock theory using empirical (= derived from experimental data),So He,Ne,Ar cannot be calculated
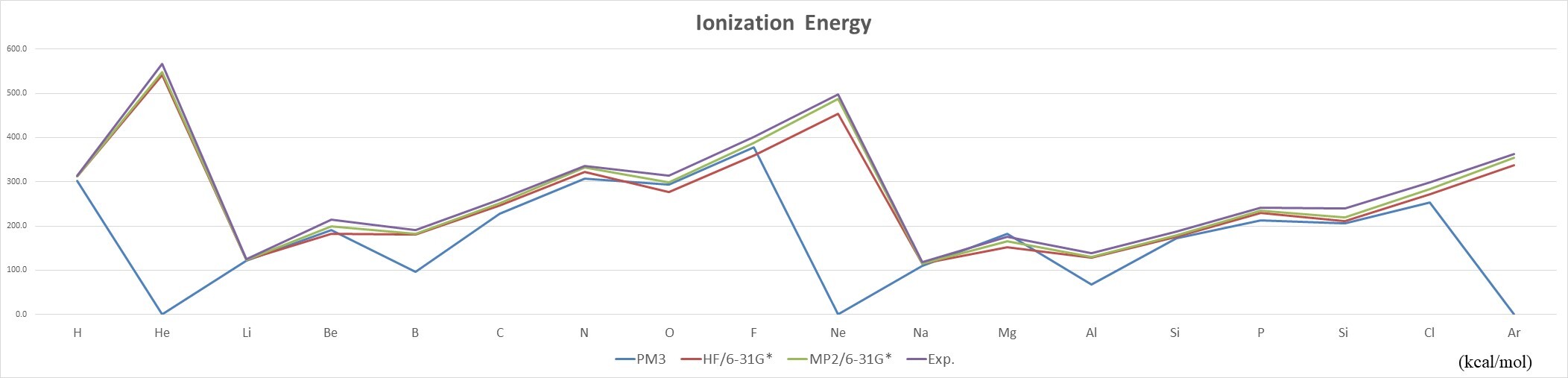
- Result
ref :https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/ASD/ionEnergy.html
Ionization energy: The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom in the ground state gas phase.
A→A++e-
|
(kcal/mol) |
PM3 |
HF/6-31G* |
MP2/6-31G* |
Exp. |
|
H |
301.5 |
312.6 |
312.6 |
313.6 |
|
He |
N/A |
540.6 |
547.7 |
567.3 |
|
Li |
122.2 |
122.9 |
122.9 |
124.3 |
|
Be |
190.3 |
182.9 |
199.4 |
214.9 |
|
B |
97.1 |
180.7 |
182.4 |
191.2 |
|
C |
227.4 |
247.1 |
252.2 |
259.6 |
|
N |
306.3 |
322.1 |
332.6 |
335.1 |
|
O |
294.4 |
276.9 |
298.5 |
313.9 |
|
F |
378.0 |
359.5 |
387.6 |
401.7 |
|
Ne |
N/A |
453.5 |
487.4 |
497.2 |
|
Na |
110.0 |
114.3 |
114.3 |
118.3 |
|
Mg |
182.9 |
152.3 |
166.1 |
176.2 |
|
Al |
68.0 |
128.1 |
130.2 |
137.9 |
|
Si |
172.3 |
176.0 |
179.7 |
187.9 |
|
P |
212.0 |
229.3 |
235.0 |
241.7 |
|
Si |
206.5 |
210.9 |
218.6 |
238.9 |
|
Cl |
253.1 |
271.7 |
283.6 |
298.9 |
|
Ar |
N/A |
338.0 |
353.9 |
363.2 |
|
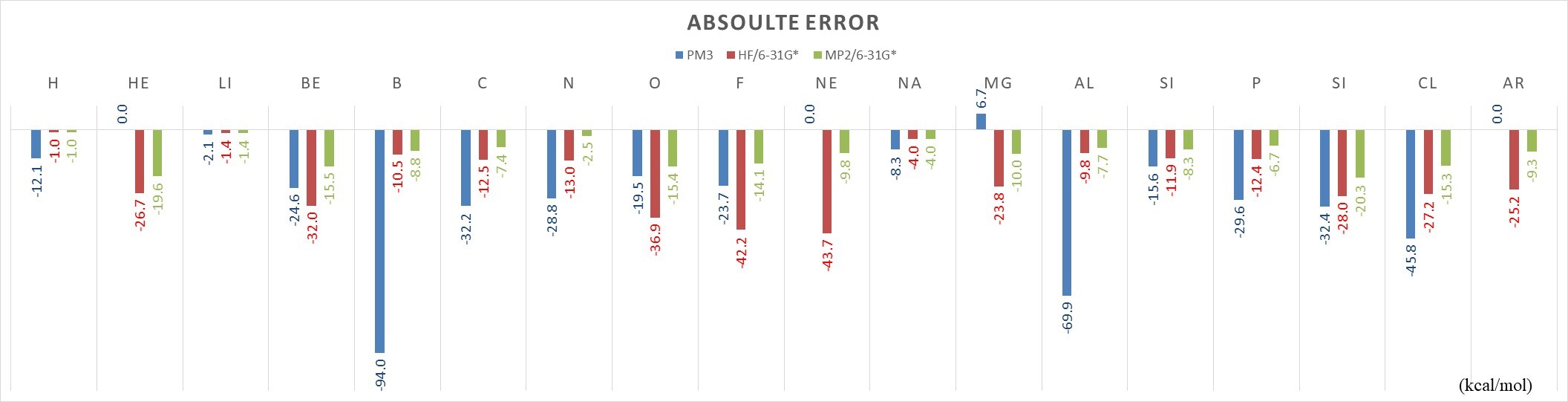
MUE |
29.7 |
20.1 |
9.8 |
|
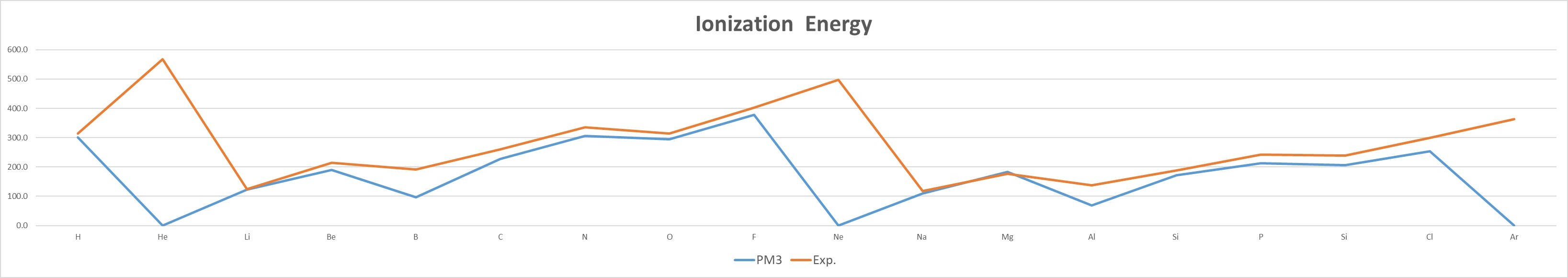
- Conclusions
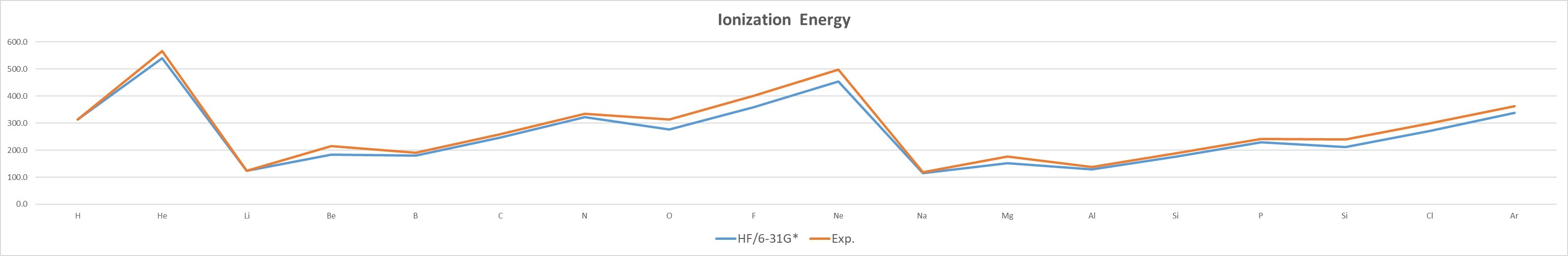
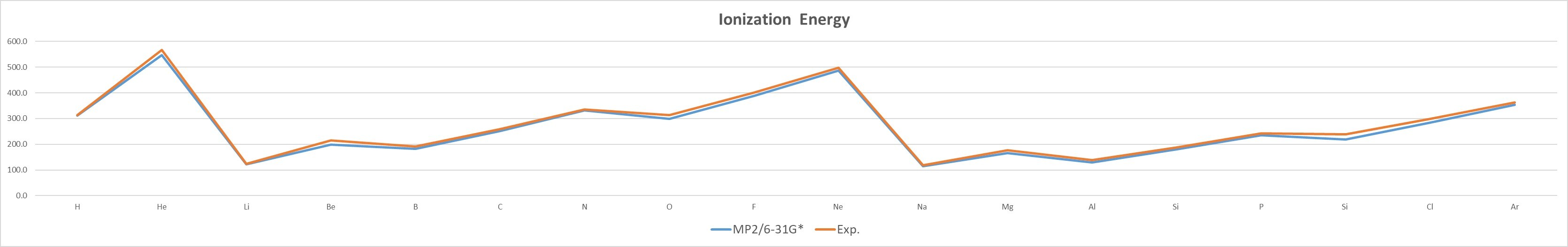
- The IE of the same group of elements decreases with increasing atomic number,as n increases, the electron is farther away from the nucleus, and the attractive force is smaller.
- The IE of elements of the same period increases with the increase of atomic number,the attractive force pull of the atomic nucleus on the electron increases.引
- Mean unsigned error (MUE): PM3 (29.7 kcal/mol) > HF (20.1 kcal/mol) > MP2 (9.8 kcal/mol)