
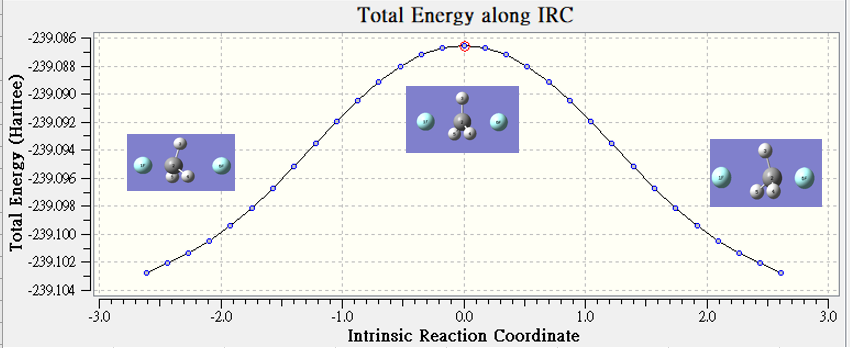
•Find the transition state and calculate the barrier height for CH3F + F− → CH3F + F− with following model.
Model:Gas/Microsolvation/Continuum Model ( PCM,sovlent=Water )
Gas(nonsolvation)
| hartree | |
| TS | -239.087 |
| reactant | -239.103 |
| Barrier Height | 0.016 |
不考慮溶劑的存在
Microsolvation
| hartree | |
| TS | -315.373 |
| reactant | -315.405 |
| Barrier Height | 0.032 |
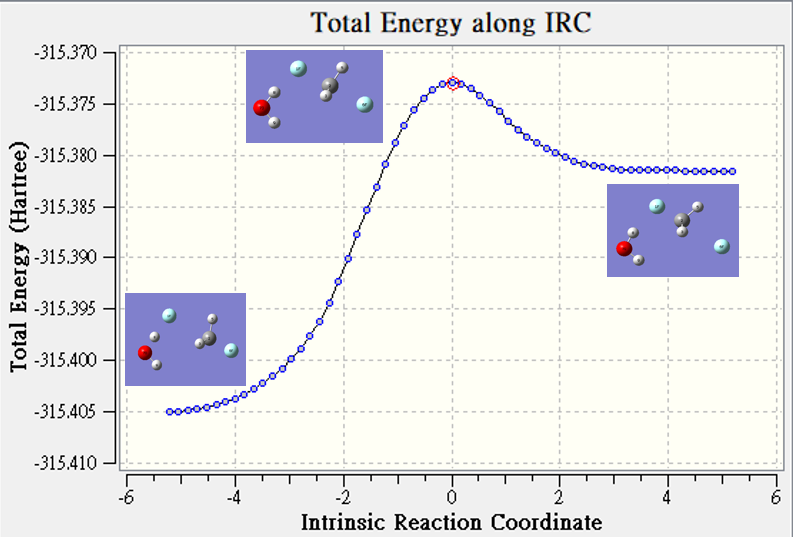
微溶合(Microsolvation)
是將幾個溶劑分子直接附著在溶質分子上,並直接以氣態的量化計算來探討分子性質的變化或對化學反應的影響。
Continuum
| hartree | |
| TS | -239.087 |
| reactant | -239.105 |
| Barrier Height | 0.018 |
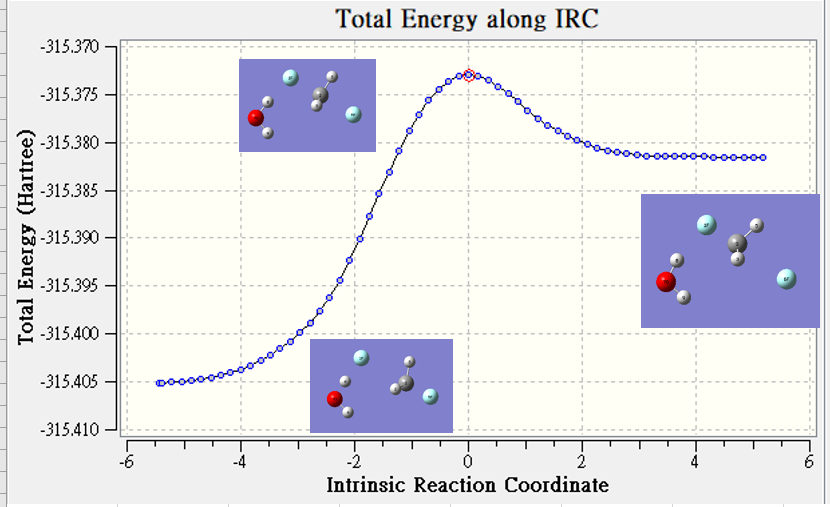
連續介質模型是將溶劑看成一個無結構均相連續的介質,不同溶劑的差別在 於介電常數 ε 的不同。
Continuum model 的重點在於溶質分子的電荷分布極化 了溶劑分子,此極化作用產生了一個電場稱為 Reaction Field,
此電場與溶質分 3 子的電荷分布作用進一步降低了溶質分子的能量,此稱為溶合效應的靜電貢獻 (electrostatic contribution) 通常也是最重要的貢獻。
Nonsolvation 是指分子在溶液中基本上不與溶劑發生相互作用,Microsolvation 是指溶質和少量溶劑分子之間可能存在微小的相互作用,而 Continuum model 則是一種將溶液中的溶質和溶劑視為連續介質來描述的簡化模型。
The experiment demonstrates that the solvation effects are important factors to consider when studying the reaction CH3F + F- → CH3F + F-.
The solvation effects can vary depending on the model used to describe the solvent, and they can affect the barrier height of the reaction significantly.
Therefore, it is necessary to choose an appropriate solvation model that can accurately capture the solvation effects for the reaction of interest.
https://lab409chem.ccu.edu.tw/p/404-1080-51826.php?Lang=zh-tw