
Calculate the k(rate constant) in different temperature for the following reaction and plot of ln(k) versus 1000/T then compare with the experimental values.
reaction :
CH4 +OH․→ H2O + CH3․
NH3 +OH․→ H2O + NH2․
method:
MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ
CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ
step:
1.Use the temperature command temperature=xxK to add to the input file.
2.Calculate the k( rate constant ) by
3.compare the differences by using the different Electronic Energies from MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ、CCSDT/aug-cc-pVTZ//MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ
result:
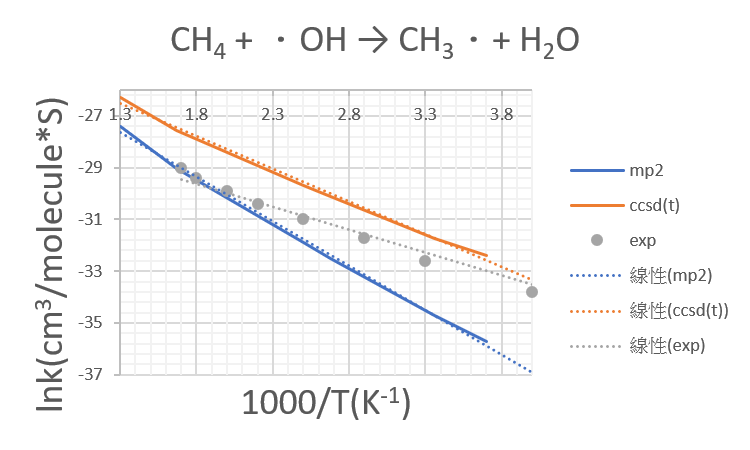
1.CH4 +OH․→ H2O + CH3․
| 1000/T | mp2 | ccsd(t) |
| 3.7 | -35.7 | -32.4 |
| 3.36 | -34.7 | -31.73 |
| 2.68 | -32.52 | -30.12 |
| 2.5 | -31.9 | -29.7 |
| 1.67 | -29.04 | -27.55 |
| 1.3 | -27.4 | -26.3 |
| CH4 | |||
| Exp | |||
| T | k | 1000/T | lnk |
| 100 | 8.20E-20 | 10 | -43.9 |
| 150 | 2.30E-17 | 6.7 | -38.3 |
| 200 | 4.10E-16 | 5 | -35.4 |
| 250 | 2.10E-15 | 4 | -33.8 |
| 300 | 6.70E-15 | 3.3 | -32.6 |
| 350 | 1.60E-14 | 2.9 | -31.7 |
| 400 | 3.40E-14 | 2.5 | -31 |
| 450 | 6.30E-14 | 2.2 | -30.4 |
| 500 | 1.05E-13 | 2 | -29.9 |
| 550 | 1.64E-13 | 1.8 | -29.4 |
| 600 | 2.44E-13 | 1.7 | -29 |
Unit:kcal/mole
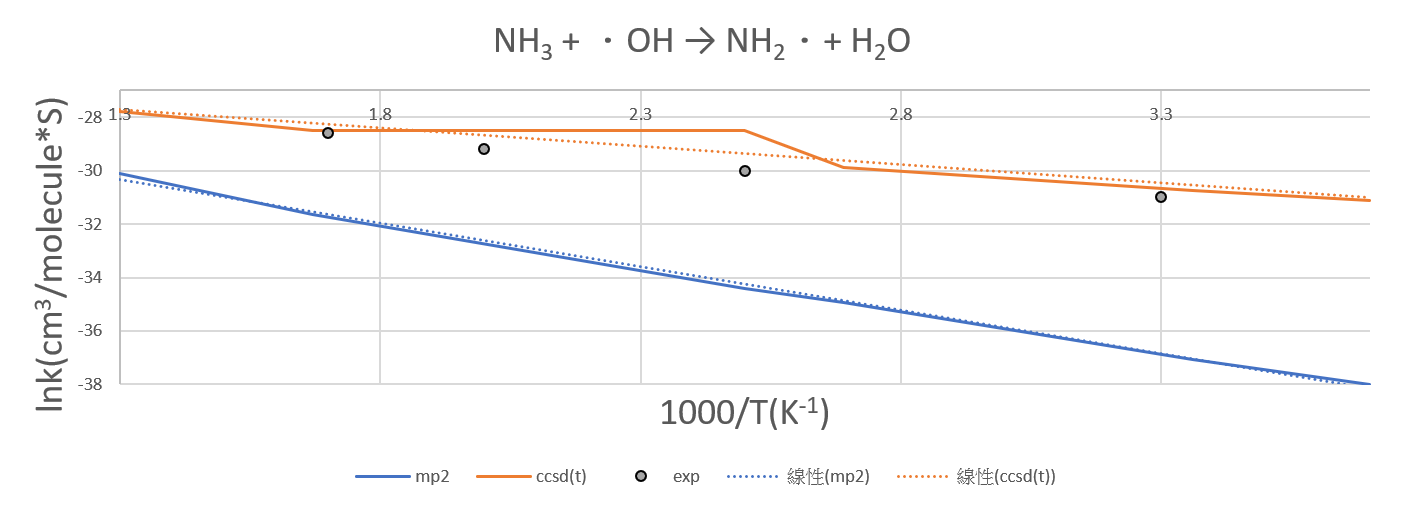
2.NH3 +OH․→ H2O + NH2․
| 1000/T | mp2 | ccsd(t) |
| 3.7 | -38 | -31.1 |
| 3.36 | -37.06 | -30.75 |
| 2.69 | -34.94 | -29.9 |
| 2.5 | -34.4 | -28.5 |
| 1.67 | -31.64 | -28.5 |
| 1.3 | -30.1 | -27.8 |
| NH3 | |||
| Exp | |||
| T | k | 1000/T | lnk |
| 200 | 7.90E-15 | 5 | -32.5 |
| 300 | 3.60E-14 | 3.3 | -31 |
| 400 | 9.60E-14 | 2.5 | -30 |
| 500 | 2.00E-13 | 2 | -29.2 |
| 600 | 3.60E-13 | 1.7 | -28.6 |
Unit:kcal/mole
參考資料